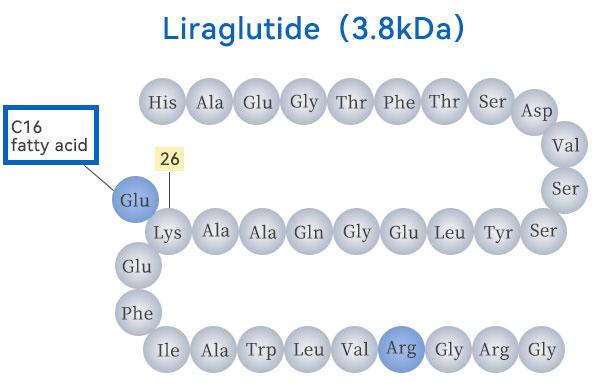
GLP-1
GLP-1 (Glucagon-like peptide-1) is a hormone secreted by intestinal cells that stimulates insulin release after meals to lower blood glucose levels.
The production of GLP-1 drugs, which are peptides comprising multiple amino acids, is complex and involves two primary methods: Bio-fermentation Synthesis and Chemical Synthesis. Both methods ultimately require downstream processes like chromatography and ultrafiltration (UF) for final drug purification and concentration adjustment.